Industrial Switches are also called industrial Ethernet switches. Because of the selected Internet specifications, they are open, widely used, high-quality and low-cost, and use the fully transparent and unified TCP/IP protocol. The Ethernet interface has already become a key wireless communication module for industrial manipulation.As the use of industrial switches becomes more and more frequent, many of its technical terms make us feel a little confused in the process of using them. Among them, the two technical terms, collision domain and broadcast domain, are relatively common. So, what is the industrial switch collision domain and broadcast domain?
Industrial Switches Broadcast domains
Broadcast domain: Based on the second layer (data link layer), a collection of all devices in the network that can receive broadcast frames sent by any device. The broadcast domain is the range of ports that broadcasts can reach.A broadcast domain is theoretically a logical group of electronic computers that receive a combination of connection points for broadcast program information.For example, if each connection point in the combination transmits a broadcast program frame, all other connection points that can receive this frame are considered to be part of the broadcast program frame.Because many devices are very easy to cause broadcast programs, if they are not maintained, it will consume a lot of broadband networks and reduce the high efficiency of the Internet.Because the broadcast domain is considered to be the second layer definition in OSI, the connection points of the first and second layers such as hubs and network switches are all considered to be the same broadcast domain.On the other hand, wireless routers and Layer 3 switches can divide broadcast domains, that is, they can connect different broadcast domains.VLAN is used to divide a large Internet into several small Internet networks, that is, it has the function of dividing several broadcast domains and reducing the size of broadcast domains.Since it is not possible to communicate immediately between different VLANs, the communication between VLANs must use a Layer 3 router, just like the connection between different netmasks. Therefore, VLANs are not live broadcast program packages, and can have smaller broadcasts Domain efficacy.
The most typical device in the broadcast domain is a switch (not including a layer 3 switch). Let's look at the working principle of a switch: a switch works on the second layer of the OSI reference model, that is, the data link layer.The CPU inside the switch will form a MAC table by mapping the MAC address to the port when each port is successfully connected.In the future communication, the data packets sent to the MAC address will only be sent to its corresponding port, not all ports; if the destination MAC does not exist, it will be broadcast to all ports, and the switch will "learn" after the receiving port responds. New MAC address and add it to the internal MAC address table.Therefore, a switch can be used to divide data link layer broadcasts, that is, collision domains; but it cannot divide network layer broadcasts, that is, broadcast domains.
Although industrial switches can isolate conflicts, so that all devices connected to the same switch do not need to consider whether other devices are sending and receiving data, but when the switch receives a broadcast signal, it will send and receive data to all the devices connected to the switch. Devices send broadcast signals. If there are too many devices, the broadcast data will flood the entire network and cannot be processed, occupying a lot of network resources, and even causing network paralysis, then a broadcast storm will be formed.How to avoid broadcast storms?Think about it, since the equipment on the second floor cannot be solved, what should we do?Yes, using the three-layer (network layer) equipment to solve the problem, the router came into being.
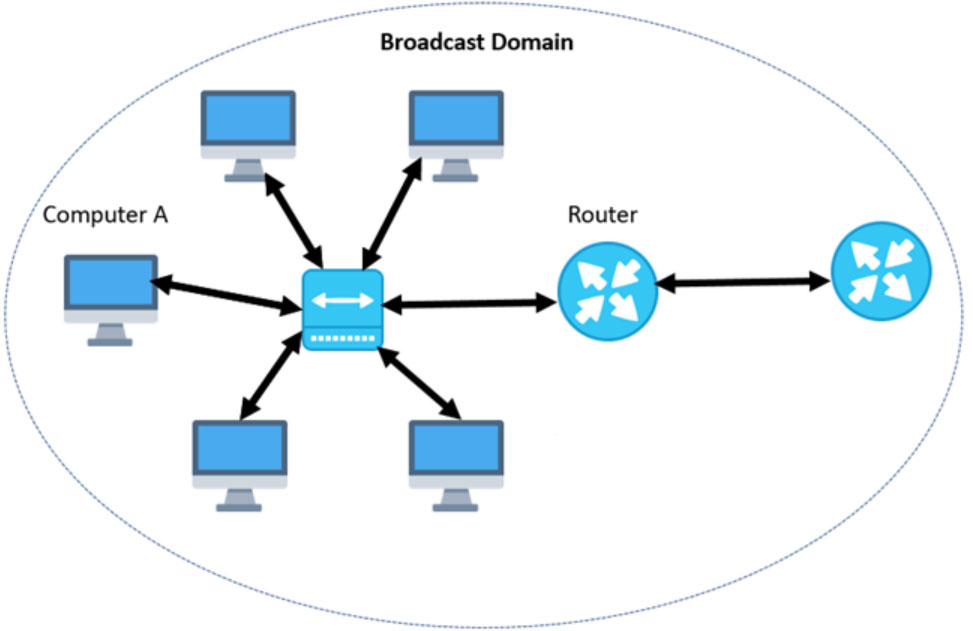
In the above-given image, you can see “Computer A” is sending a broadcast, and the switch will forward it to all the ports. Every connected switch will get a copy of the broadcast packet. Here, all the switches will flood the broadcast packet to all types of ports.
Industrial Switches Collision Domains
Collision domain: Based on the first layer (physical layer), every node in the same collision domain can receive all transmitted frames.Collision domain is a physical means that refers to the combination of all websites connected to the same physical medium.There is a substance contention among such sites (such as the basic principle of CSMA/CD substance inspection in traditional Ethernet interfaces), that is, they must share a certain part of the common substance of resources during data communication.Conflict domains refer to the fewest domains that are less prone to conflict.When electronic computers and other devices in the same conflict domain are interconnected, only the data information pushed by one device is allowed to pass through this channel according to the same physical channel at the same time, and the data information pushed by other devices will not be sent until this point. A channel can only pass when it is "idle", otherwise conflicts will occur, and at this time, it is very likely that many data files will be lost or lost due to delays.The size of the collision domain can take into account the characteristics of the device. We know that the previous network switches and wireless amplifiers are all typical centralized connection devices that share resource materials, and they are all working on the first layer of OSI/RM-physical layer. equipment.Other devices connected to this kind of equipment are all in the same collision domain, and the collision domain cannot be divided, that is, the data information message format on all ports needs to wait in a long queue to pass.
At work, devices on the second layer of OSI/RM - the data link layer, such as bridges and industrial switches, also have the definition of conflict domains, but they are all capable of dividing conflict domains and connecting different conflict domains. .If we regard the transmission channel on the network switch and wireless amplifier as a cable, then the interchange channel of the bridge and the network switch can be regarded as a bundle of cables, with several separate channels (it is a drainage matrix design plan), which allows for multiple communications at the same time.
The bridge is similar to the wireless amplifier. The traditional bridge has only 2 ports, which can be used to connect different subnets.That is, the bridge can be regarded as a device that can connect two collision domains.The 2 subnets connected to the same bridge each become a collision domain.The industrial switch is an extension of the bridge. It has many ports, and each port is a collision domain, that is, the remote data transmission of one or several ports is not easy to harm the transmission of other ports, because the data pushed by different ports Messages are not queued on the same channel, but only data messages on the same port are queued on the matching port channel.
The most typical device in the collision domain is the hub, so what is the working principle of the hub? The hub (hub) is a pure hardware network bottom device, and basically does not have the 'smart memory' capability and 'learning' capability similar to the switch.It also does not have the MAC address table that the switch has, so when it sends data, it is not targeted, but is sent by broadcasting.That is to say, when it wants to send data to a node, it does not directly send the data to the destination node, but sends the data packet to all nodes connected to the hub.
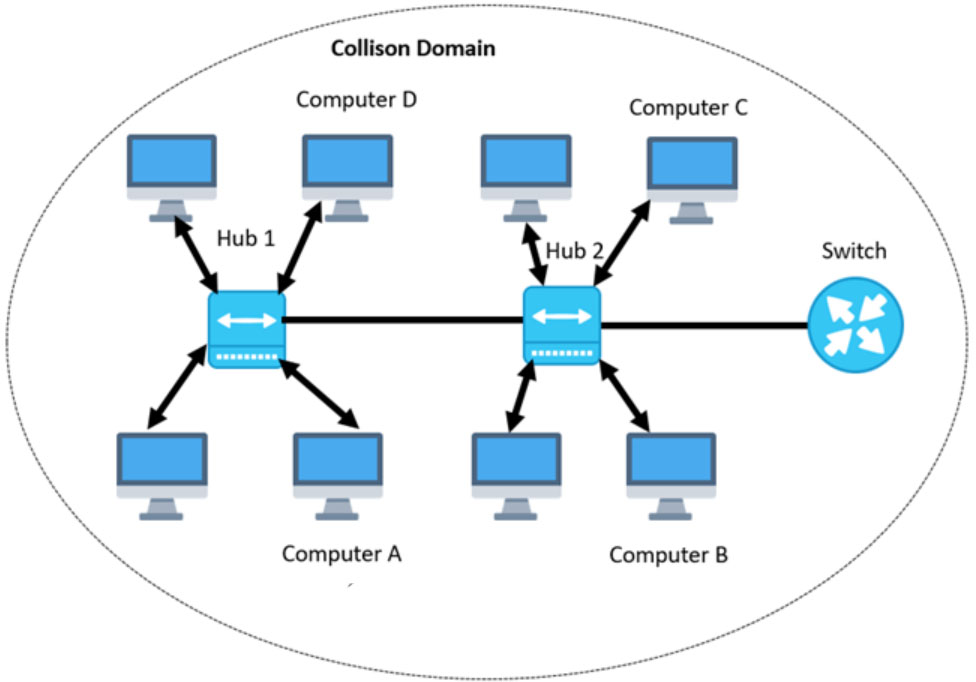
Above given image is an example of a collision domain. In the above example, you can see “Computer A” send a data signal to “Computer C.” In the same way, “Computer B” sends a data signal to “Computer D” where a Collision will happen.
Contact: sales
Phone: 18688787693
E-mail: sales@hsindustrialswitch.com
Add: Room 608, Building B,GaoXinQi TEC Park,Baoan District, ShenZhen,China